Using CP/M
CP/M Quick Reference
Control key commands
CTRL + C |
Restarts CP/M by initiating a warm start |
CTRL + E |
Forces the cursor to the next line of the screen for continued command line input. |
CTRL + H |
Moves the cursor one space to the left in the same manner as the BS key. |
CTRL + I |
Inputs a tab code (same as the TAB key) |
CTRL + P |
Turns on or off the printer echo function. When the printer echo function is turned on, data displayed on the LCD screen is output to the printer (or other device assigned to LST:) each time the RETURN key is pressed. The printer echo function is turned on by pressing CTRL + P once and is turned off when CTRL + P is pressed a second time. (Make sure the printer is connected properly before using this command.) |
CTRL + R |
Redisplays the contents of the current command line. |
CTRL + S |
Momentarily stops processing currently being performed (same as the PAUSE key). Processing can be resumed by inputting this command again. |
CTRL + U |
Cancels the current command line and moves the cursor to the next line on the screen for input of a different command. |
CTRL + X |
Erases the current command line and moves the cursor back to the beginning of the line. |
CTRL + Z |
Terminates input from the keyboard (used in combination with certain CP/M transient commands). |
Commands
d: - A drive letterfilematch - an exact filename, or a wildcard match for files.
Items such as [item] are optional, ones such as <item> are compulsory.
DIR [d:][filematch]
Display a list of files in the specified, or current drive.
ERA [d:]<filematch>
Erase specified files. filematch *.* can be used to match all files in the current drive.
REN [d:]newname.ext = oldname.ext
Change the name of a disk file from oldname.ext to newname.ext
SAVE n [d:]filename.ext
Save the specified n number of pages of the transient program area to disk under the specified file name.
TYPE [d:]filename.ext
Display the contents of the specified file on the display screen. Display is only meaningful if the file contents was ASCII text.
USER n
Switches to the specified user area in a disk drive.
A user area is a physical area on a disk which has its own directory and which is managed separately from the rest of the disk. Data cannot be read from or written to any user area other than that in which CP/M is currently operating. A disk can be divided up into a maximum of 16 user areas.
PIP
Copy FOO.TXT to console (print).
C:PIP CON:=A:FOO.TXTWrite to file from terminal (CTRL-Z to EOF, CTRL-M+J for new line):
C:PIP FOO.TXT=CON:Copy file from current drive to A:
C:PIP A:UPLOAD.COM=UPLOAD.COMED
- http://www.gaby.de/cpm/manuals/archive/cpm22htm/ch2.htm
Commands mode
#a |
load all lines from file (given as arg to the command) to memory |
10a |
load 10 lines from file |
b#t |
go to beginning, print all lines |
b |
go to beginning |
n or -n |
move n lines ahead/behind and print |
t |
print current line |
k |
kill current line |
i |
insert before current line |
e |
save and exit |
o |
discard changes |
In insert mode
CTRL + H |
backspace one char |
CTRL + Z |
exit insert mode |
ASM
Compile and run example program:
c:asm example
c:load example
exampleShow compiled program listing:
type example.prnCompiler output line markers
S |
syntax error |
L |
bad label |
E |
bad expression |
R |
bad register |
Y |
bad value |
API
- https://www.seasip.info/Cpm/bdos.html
- https://obsolescence.wixsite.com/obsolescence/cpm-internals
- http://www.gaby.de/cpm/manuals/archive/cpm22htm/ch5.htm
Entry point: 05h (CALL 05h).
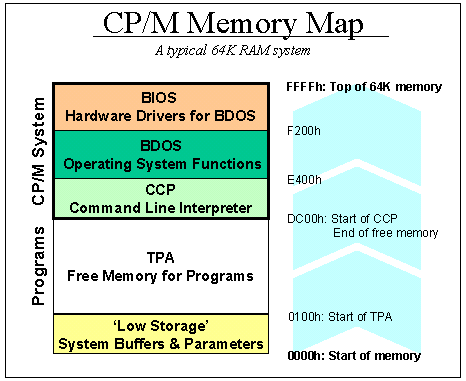
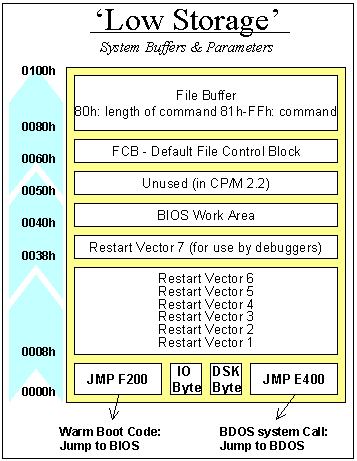
Memory map
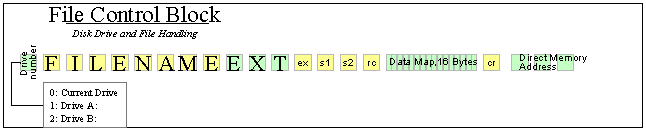
File Control Block
FCB start: 5Ch (not 60h as in the picture).
| Address | Field | Definition |
|---|---|---|
FCB+00h |
dr | drive code (0-16) 0 = use default drive for file 1 = auto disk select drive A, 2 = auto disk select drive B, ... 16 = auto disk select drive P. |
FCB+01h |
f1...f8 | contain the filename in ASCII upper-case, with high bit = 0 |
FCB+09h |
t1,t2,t3 | contain the filetype in ASCII upper-case, with high bit = 0. t1', t2', and t3' denote the bit of these positions, t1' = 1 = Read-Only file, t2' = 1 = SYS file, no DIR list |
FCB+0Ch |
ex | contains the current extent number, normally set to 00 by the user, but in range 0-31 during file I/O |
FCB+0Dh |
s1 | reserved for internal system use |
FCB+0Eh |
s2 | reserved for internal system use, set to zero on call to OPEN, MAKE, SEARCH |
FCB+0Fh |
rc | record count for extent ex; takes on values from 0-127; Set this to 0 when opening a file |
FCB+10h |
d0...dn | filled in by CP/M; reserved for system use |
FCB+20h |
cr | current record to read or write in a sequential file operation; normally set to zero by user after opening file |
FCB+21h |
r0,r1,r2 | optional random record number in the range 0- 65535, with overflow to r2, r0, r1 constitute a 16-bit value with low byte r0, and high byte r1 |
File Buffer start: 80h (128 bytes long).
Notes
- When running command in CP/M with file path as first argument the drive number and file name are set in default FCB automatically before program runs.
- When two arguments are given another drive number and file name are set starting from absolute
6Ch. It will be overwritten by file operations. - If no arguments are given the FCB file name is all blank/space characters (
- Command line arguments are also available from
80h(File Buffer).
Useful constants:
FCB EQU 5Ch ; File Control Block
FCBFNAME EQU FCB+01h ; FCB File Name
FCBEX EQU FCB+0Ch ; FCB Excent Number
FCBRC EQU FCB+0Fh ; FCB Record Count
FCBCR EQU FCB+20h ; FCB Current Record
FB EQU 80h ; File BufferCP/M procedures
| Function Number |
Function Name |
Input | Output | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dec | Hex | |||
| 0 | 0 | System Reset | none | none |
| 1 | 1 | Console Input | none | A = ASCII char |
| 2 | 2 | Console Output | E = char | none |
| 3 | 3 | Reader Input | none | A = ASCII char |
| 4 | 4 | Punch Output | E = char | none |
| 5 | 5 | List Output | E = char | none |
| 6 | 6 | Direct Console I/O | E = 0FFH (input) | A = char |
| E = 0FEH (status) | A = status | |||
| E = char | none | |||
| 7 | 7 | Get I/O Byte | none | A = I/O byte value |
| 8 | 8 | Set I/O Byte | E = I/O byte | none |
| 9 | 9 | Print String | DE = Buffer Address | none |
| 10 | A | Read Console String | DE = Buffer | Console characters in Buffer |
| 11 | B | Get Console Status | none | A = 00/non zero |
| 12 | C | Return Version # | none | HL = Version # |
| 13 | D | Reset Disk System | none | none |
| 14 | E | Select Disk | E = Disk # | none |
| 15 | F | Open File | DE = FCB address | A = FF if not found |
| 16 | 10 | Close File | DE = FCB address | A = FF if not found |
| 17 | 11 | Search For First | DE = FCB address | A = Directory Code |
| 18 | 12 | Search For Next | none | A = Directory Code |
| 19 | 13 | Delete File | DE = FCB address | A = none |
| 20 | 14 | Read Sequential | DE = FCB address | A = Error Code |
| 21 | 15 | Write Sequential | DE = FCB Address | A = Error Code |
| 22 | 16 | Make File | DE = FCB address | A = FF if no DIR Space |
| 23 | 17 | Rename File | DE = FCB address | A = FF if not found |
| 24 | 18 | Return Login Vector | none | HL = Login Vector* |
| 25 | 19 | Return Current Disk | none | A = Current Disk Number |
| 26 | 1A | Set DMA Address | DE = DMA address | none |
| 27 | 1B | Get ADDR (ALLOC) | none | HL = ALLOC address* |
| 28 | 1C | Write Protect Disk | none | none |
| 29 | 1D | Get Read/only Vector | none | HL = ALLOC address* |
| 30 | 1E | Set File Attributes | DE = FCB address | A = none |
| 31 | 1F | Get ADDR (Disk Parms) | none | HL = DPB address |
| 32 | 20 | Set/Get User Code | E = 0FFH for Get | A = User Number |
| E = 00 to 0FH for Set | none | |||
| 33 | 21 | Read Random | DE = FCB address | A = Error |
| 34 | 22 | Write Random | DE = FCB address | A = Error Code |
| 35 | 23 | Compute File Size | DE = FCB address | r0, r1, r2 |
| 36 | 24 | Set Random Record | DE = FCB address | r0, r1, r2 |
| 37 | 25 | Reset Drive | DE = Drive Vector | A = 0 |
| 38 | 26 | Access Drive | not supported | |
| 39 | 27 | Free Drive | not supported | |
| 40 | 28 | Write Random w/Fill | DE = FCB | A = error code |
Reading file
Given file name in the arguments one can first check if argument was given by checking for space character in FCBFNAME (FBC + 01h).
If file name is filled we can open the file:
XOR A
LD (FCBEX),A ; select 0'th extent
LD (FCBRC),A ; clear
LD (FCBCR),A ; clear
LD C,FOPE ; open file
LD DE,FCB ; use default FCB
CALL BDOSSet EX, RC and CR to 0 and call File Open (0Fh). A will contain FFh if file was not found.
Next file can be read:
XOR A
LD (FCBCR),A ; start from beginning
LD C,FRED ; read file
LD DE,FCB ; use default FCB
CALL BDOSSet CR to 0 to start reading from beginning of the file and call Read Sequential (14h). A is set to 0 if read was successful.
128 bytes was read to FB (starting at 80h). CR (and EX) will be automatically incremented, so calling Read Sequential again will read next 128 byte of the file to FB.